Introduction. Benign prostate hyperplasia(BPH) is the most common benign disease in American men [1]. Aproximetely, BPH affects 75 and 83% of the men in the seventh and eigth decade of life respectively. The patients with BPH usually present lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTSs). The LUTSs include storage, voiding and postvoiding associated symptoms and are seen in 30% of the men over the age of 65 years [2]. In 1992, the World Health Organization accepted to use symptom score which was developed by American Urological Association [3]. This symptom score was called International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) which includes seven questions about bladder emptying, frequency, intermittancy, urgency, weak stream, nocturia and straining [4]. A new symptom score was developed by Walt et al in 2011 that was called Visual Prostate Symptom Score (VPSS) [5]. The VPSS has advantages about simplicity and easy understandable for elderly men when comparing the IPSS [3].
In this stuy, we aimed to compare the answering of IPSS and VPSS for the patients presenting with LUTS in urban area (Çorum city) of Turkey.
Methods. Data were recorded prospectively from the patients who were admitted to Hitit Universtiy, Çorum Erol Olçok Training and Research Hospital for LUTS over the age of 45 years from February to August 2017. The patients were requested to fill the IPSS and VPSS without any assistance. The IPSS included 8 questions for irritative symptoms (2, 4, 7. questions (Qs)), obstructive symptoms (1, 3, 5, 6 Qs) and quality of life (8.Q); VPSS consisted 4 pictograms; 1 and 2 for irritative symptoms, 3 for obstructive symptom and 4 for quality of life. The education level, age and PSA level of the patients were noted. The questionnaires were evaluated for the patients completed or not with themselves. The patients who had history of prostate surgery, urethral stricture, radiotherapy and neurological disorders were excluded from the study.
The statistical analyses were performed using MedCalc Statistical Software demo version 16.2.0 (MedCalc Software bvba, Ostend, Belgium; https://www.medcalc.org; 2016). The data was expressed as mean+standard deviation and chi squared test was used for percentage, p value <0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
Results: There were 81 patients in the study. The mean age of the patients was 58.86±7.39 years. The education levels and demographic characteristics of the patients are shown in
Table 1. According to the Turkish education level; primary school (5 years), secondary school (8 years), high school (12 years) and university. 44 patients had primary, 10 had secondary and 11 patients had high school education level. There was 16 patients who had graduated from university.
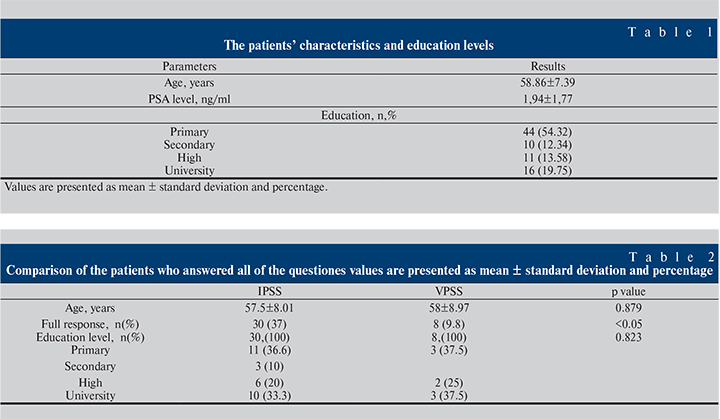
The IPSS and VPSS questionnaires were completed by 30 and 8 patients without assistance respectively. Table 2 shows the comparison analysis between VPSS and IPSS for the education levels of the patients about full complete. There was no significant difference for education level between the full complete response of questionnaires (p=0.823).
Discussion: Benign prostate hyperplasia associated LUTS is very common problem in middle age or older men [6]. The IPSS is a useful questionnaire for evaluating the severity of LUTS and treatment efficacy of BPH in follow up [7]. Therefore guidelines recommend that IPSS can be used in the evaluation and follow up period for LUTS and BPH. The IPSS includes 8 questions; the first 7 questions were to evaluate storage and voiding symptoms and the patients choose 1 to 5 point in every question [3]. The final question is about quality of life. The symptom score ≤7, 8–19, ≥20 are classifed as mild, moderate and severe symptoms. But, most patients with a low education level can not answer the IPSS questionnaire correctly, eyesight related and cognitive problems are negative factors after the age of 50 years [6]. The patients usually ask questions the health workers for the explanation of the question because of its complexity [3]. To overcome the problems, a new symptom score that called VPSS was developed by Walt et al using 4 pictograms [5]. The advantages of VPSS are simpler and easier to understand for elderly men than IPSS [3]. The pictograms represent frequency, nocturia, weak stream and quality of life.
The authors investigated the correlation between VPSS and IPSS, found that 91.3% and 77.9% (p<0.05) of the patients completed the VPSS and IPSS respectively [7]. In another study from Indonesia, the authors reported that VPSS was completed much more than IPSS [3]. Taneja et al, found that 89 patients(80.9%) completed VPSS but only 48 patients(43.63%) could completed the IPSS [6]. The education level of the patients; 54.5% was
The limitations of the current study are small patient group from one single center. The other limitaion of the study is the education level of the patients. The education level can not be similar in the population
In conclusion, we think that there are some problems to understand for IPSS and VPSS for Turkish patients. New and easily understandable questions must be preperad for using national language to understand well.



